When it comes to assessing risks in capital construction projects, one of the first tasks in the project risk management plan is to determine what will be the categories for the risks to be identified. Those would usually include the categories of political, economic, technological, legal, market, supply chain, organizational, operations, environmental, financial, resources, staffing, scheduling, reputation, processes, and systems within the organization, weather, regulations, customer, external stakeholder groups, work culture among others.
Processes and systems within the organization’s risks also cover the project management processes required to run the delivery of their capital construction projects. Those risks are no different than other risk categories, they also have cost and time impacts that could result from delayed approvals due to ineffective processes and lack of accountability, fraud due to lack of transparency among others.
Therefore, the causes that could result in threats when executing project management processes need to be eliminated. To ensure that all project management processes that need to be responded to are identified, it is recommended to start with identifying the project stages. Those would usually include the stages for planning, tender for design, design, tender for construction, mobilization, construction, testing, and commissioning, and handover. This will help in aligning identified risks with the project’s responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) to ensure that all commercial, procurement, quality, HSE, scheduling, site management, and other types of processes had been covered.
One of the project management processes that could result in additional cost and delay risks, is the Request for Information (RFI) process. In most Construction Documents (agreements, drawings, specifications, and bill of quantities), developed by the Engineer, it is inevitable that those documents will not adequately address every single matter. There may be gaps, conflicts, or subtle ambiguities. The objective of the Request for Information (RFI) is to act as the project communication management process to resolve these gaps, conflicts, or subtle ambiguities during the construction process to eliminate the need for costly corrective measures.
Although the response to the RFI could lead to additional work that represents added cost or delays to the project’s scope of work, nevertheless, the purpose of the current risk assessment for the RFI process is to analyze the risks that could lead to delays in responding to an RFI, failing to secure authorized approvals for RFIs that are either out of scope or could have cost and/or delay implications, missing or wrong information, lack or missing of supportive documents with RFI submissions, RFI review is not done by the assigned team members, lack of having the real-time insight into the volume, frequency, type and status of submitted RFIs, improper usage of RFI by the contractor to raise claims among others.
Similar to all other business processes including project management processes, an RFI process requires having a pre-defined template to capture all needed information as well as a workflow to ensure that the submission, review, distribution, and response to an RFI is carried out in accordance with the approved project management plan (PMP) also known as the Project Execution Plan (PEP). The RFI template should include as a minimum the fields for the project name, issuance date, RFI ID, issued by who, issued to who, CSI specification reference as well as a reference to all relevant contract documents such as drawings, specifications, and bill of quantities, question or query, answer or response, date response needed, date response is given and list of attached documents. Nevertheless, the RFI template can be improved by adding the fields for the relevant Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) level, project schedule activity that its start date is affected by the RFI, the reason for submitting the RFI, location of the work associated with RFI, building system discipline that the RFI relates to, the proposed solution for the raised query or question, whether the RFI entails new scope of work or not, whether the RFI has cost impact or not, whether the RFI has time impact or not, among others.
The RFI workflow should detail the sequence of the tasks to be followed in the submission, review, distribution, and response for each RFI. The workflow should also include decision points for RFIs that could have cost and/or time impact. The workflow could also detail the link with other project management processes like for example the change order process in case the RFI response entails an additional scope of work that the contractor needs to be compensated for.

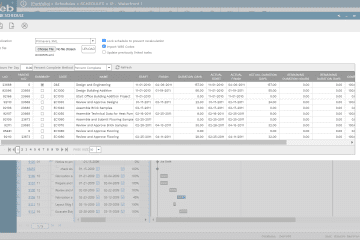
Using a Project Management Information System (PMIS) like PMWeb, the RFI process and all other project management processes can be automated to help in eliminating and/or mitigating the risks associated with performing the process. Using the PMWeb ready-to-use RFI module, all needed information fields for the RFI template can be made available. For the default fields such as Project, Phase, WBS level, Project Schedule Activity ID, CSI Specification, Discipline, Trade, Priority among others, the values will be available from the relevant list of values. For newly created fields such as building, floor, and room location, a predefined list of values will be created to standardize the values of captured information.

To fulfill the requirements for attaching all referenced documents in the RFI, PMWeb allows attaching all supporting documents directly into the RFI or attaching documents that are already uploaded and stored into the PMWeb document management repository. For picture and PDF file formal documents, PMWeb allows displaying those on the RFI form main page. In addition, PMWeb allows linking relevant records of other project management processes to the RFI as well as imported MS Outlook emails.

Since the RFI form will involve different project entities when it comes to providing the needed content, edit and view permission rights need to be adjusted to reflect the role of those entities. The permission rights should be aligned with the project’s responsibility assignment material and workflow tasks assigned to the RFI process.

The next step is to automate the workflow tasks using the PMWeb workflow module. The workflow will identify the tasks, sequence, accountability, and duration of tasks needed to submit, review, and approve the RFI process. Those tasks will be assigned to their responsible project team members in accordance with the project’s responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) to ensure that the RFI review process is aligned with the building system discipline it belongs to as well as the set authority approval levels. The workflow will be aligned with permission rights assigned to the RFI module.

When the RFI is formally submitted using PMWeb, the RFI workflow tab will keep track of the review and approval process by capturing the planned due action due date, taken action, username, actions date and time, comments among others. The status of the RFI will be automatically adjusted to reflect the current workflow status.

The workflow tasks details for the RFI process and all other project management processes that are automated in PMWeb will become available to be reported on in any desired form or format. For example, delayed workflow tasks can be colored in red, due workflow tasks in yellow, and not due tasks in green. The workflow tasks can be grouped by process name, user name, project or any other workflow category. PMWeb comes ready with its own workflow status report that can be used as-is.

For project management processes that require formal submission like the Request for Information (RFI), there will be the requirement to have a hard copy output that is wet-signed and stamped or an electronic PDF file version copy that can be digitally signed using DocuSign or others. PMWeb report writer allows designing the output format in any desired form and format to comply with the project communication requirements as well as the project’s branding requirement. In addition, tabular and graphical reports can be created to report on the performance of all automated project management processes including the RFI process.

The data captured in the RFI process can be used by the project team to analyze and identify trends on RFIs growth, turnaround time, reasons for issuing the RFIs, contractor issuing RFIs, design consultant among others. This analysis can be further improved when the RFI process data is based on the data from the complete projects’ portfolio has whether those were current or completed projects. Actually, the analysis data can be enriched by adding relevant data from other sources. Using business intelligence and data visualization solutions like MS Power BI, the project team can query or import the project management processes data and run the required analysis reports.

Finally, the project dashboard will provide an overall status of the implemented project management process including the Request for Information (RFI). The project dashboard will be configured to enable the stakeholder to drill down to the REI register to have an overall review of how this process is performing with the option to further drill down to any RFI transaction to review further details when need. The drill-down process can be configured to enable reaching the PMWeb RFI transaction to view attached documents, linked records, and workflow history.