Risk buffering (or risk hedging) is the creation of some reserve or buffer that can absorb the effects of the many accepted risks without jeopardizing the project successful delivery. Project contingency or buffering also includes the allocation of additional time for the project’s completion. Nevertheless, the risk that those organizations could face, and many times is not accounted for, is the risk of falling short when it comes to consuming the cost and schedule buffer during the project’s execution. A project management information system (PMIS) is needed to manage, monitor, evaluate and report project contingency drawdown.
Quantifying the Right Cost and Schedule Buffer
Regardless who is managing the projects, the need date to finish the project on time and within the approved budget always remains. To start with, we need to have a correct and realistic integrated project schedule that is linked to the project budget. The project schedule, which gets detailed to the desired control level, will be modified to include all risk response actions that relate to avoidance, mitigation and transfer of risks. In other words, it will only be used to analyze the risk uncertainties that the organization’s responsible for the project delivery has to accept and cannot be mitigated. For each activity, we need to determine the worst case scenerio for duration as well as the most likely and optimistic duration to execute the activity and budget to deliver the associated scope of work. The schedule also includes all risk events that cannot be avoided, mitigated or transferred.
Using a Monte Carlo simulation tool like Safran Risk, Primavera Risk Analysis or Acumen Risk, the risk probability cumulative distribution curve gets generated. The organization needs to determine the confidence level that enables setting the project’s target completion date and budget for delivering the project’s scope of work. Usually, this is set at 80% confidence level where the difference between this 80% confidence level and 100% confidence level will be the cost and schedule buffer.

Freezing the Project’s Approved Execution Plan
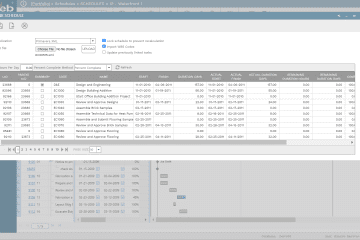
PMWeb project management information system (PMIS) will be used to capture the details of the approved 80% (or whatever selected percentage) confidence plan. PMWeb budget module captures the approved budget and schedule start date for the project’s execution plan. The budget aligns with the project WBS levels where the project is controlled at. In addition, the project budget includes the contingency as a separate line item number, with the option to breakdown the overall contingency into more detailed controlled levels. Accordingly, the total of this approved budget equals the 100% confidence level budget and project completion date. Similar to all PMWeb modules, documents can be uploaded and attached to the budget as well as relevant PMWeb records can be linked. In addition, an assigned workflow formalizes the steps for submitting, reviewing and approving the project budget before it is used for managing the project’s contingency.

Managing the Consumption of Contingency and Buffer
At the end of each progress review period which could be weekly, bi-weekly or monthly, the total of consumed buffer gets captured using PMWeb budget request module. For each contingency or buffer usage, there will be a separate budget request form for which it will show the additional cost and schedule adjustment for the relevant project WBS level and the adjustment to the cost and schedule buffer for the same WBS level. The total sum value of each budget request will be always zero. Similar to all PMWeb modules, documents can be uploaded and attached to the budget requests as well as relevant PMWeb records can be linked. In addition, a workflow will be assigned to formalize the steps for submitting, reviewing and approving the project budget before it is used for managing the consumption of the project’s contingency. PMWeb conditional workflow allows adding the different rules that are aligned with the approval authority levels set for the project.

Monitoring, Evaluating and Reporting Cost Contingency and Schedule Buffer Status
The Cost and Schedule Buffer Status dashboard provides real-time single version of the truth of a project buffer status. The dashboard includes a log of all budget adjustments that are related to buffer consumption, current cost and schedule buffer consumed and available for each project stage.

In addition, users can create another dashboard to report on the Cost and Schedule Buffer Status for the complete projects’ portfolio of the organization. This provides executive management with an understand of the amount of contingency funds consumed and blocked for each project. At this executive level, the organization might also consider the management reserve they have allocated to each project to address the impact of risks that cannot be managed at the project level.

Risk buffering is the creation of some reserve or buffer that can absorb the effects of the many business risks that construction project owners must accept without jeopardizing the project. Buffering can also include the allocation of additional time for the project’s completion. Nevertheless, the risk that those organizations could face and is many times not accounted for is the risk of falling short when it comes to consuming cost and schedule buffer during the project’s execution. A PMIS like PMWeb properly establishes, monitors, evaluates and reports contingency usage to reduce the risk of the project running out of money before the project is complete.