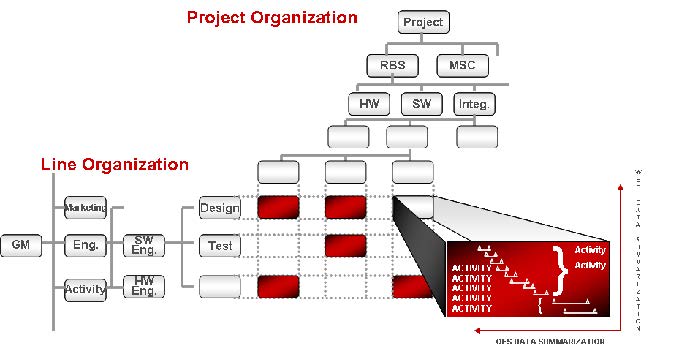
Intelligence, whether artificial or not, depends on the extent of relevant wisdom available to propose actions or predict future outcomes. Wisdom depends on the extent of available knowledge which depends on the amount of valid information available that depends on the trustworthiness of historical and current data that can be extracted, transferred, and loaded from the sources where data is captured. Although the volume of data available to be extracted is massive, nevertheless, when it comes to capital construction projects, what matters most is the quality of this data.
Data quality is important when applying artificial intelligence techniques because the results of these solutions will be as good or bad as the quality of the data used. Erroneous or incomplete data is of no value when it comes to making decisions. The algorithms used on Artificial Intelligence can only assume that the data to be analyzed are reliable. Then, if they are erroneous, the results will be misleading and the decision-making process will be compromised.
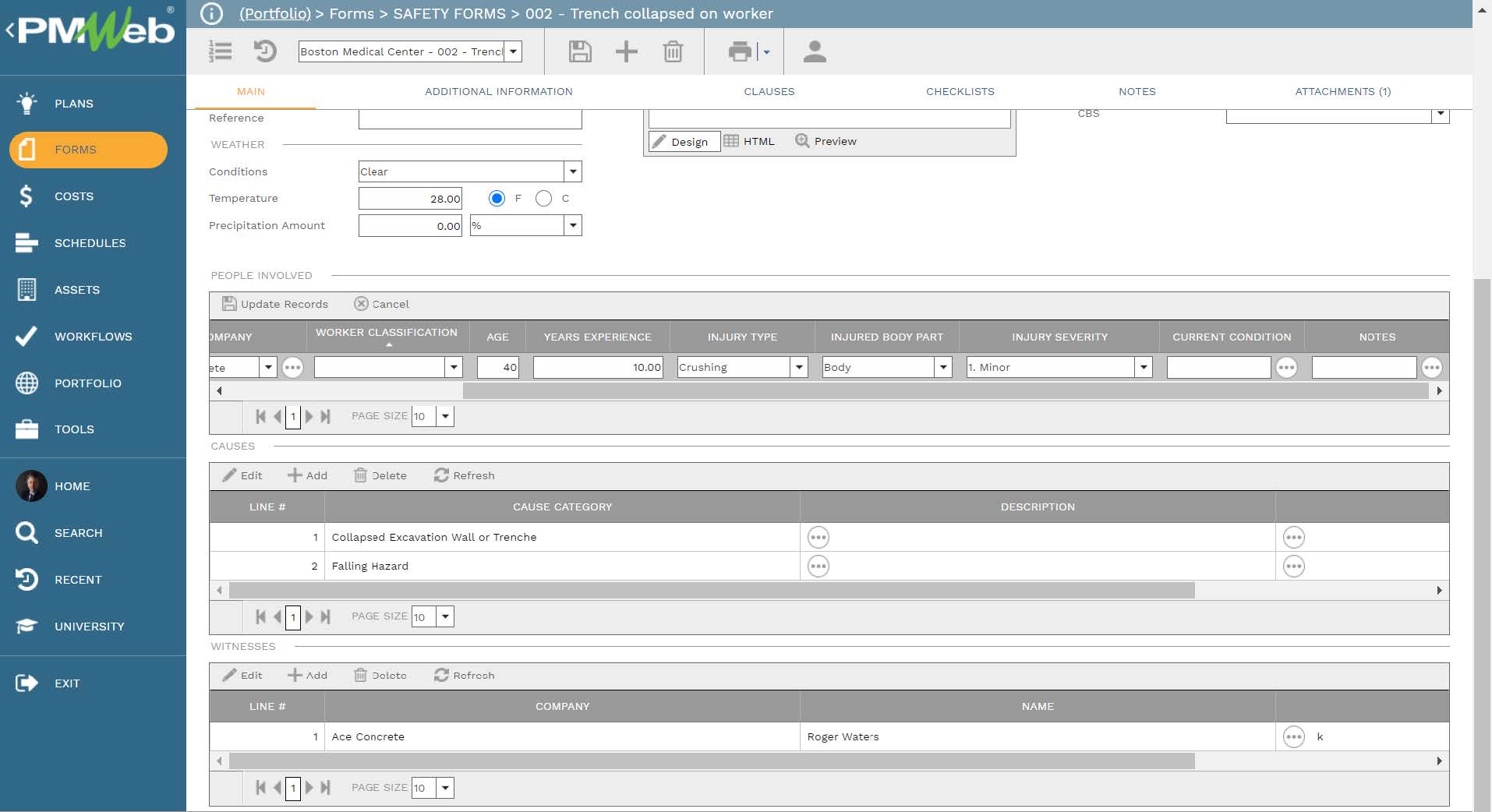
The use of artificial intelligence to improve safety on sites is one of the areas that will add value to the delivery of capital construction projects. Nevertheless, the data needed for better AI should go beyond the data associated with safety incidents where the description of the instance, date and time of the instance, location of the instance, weather status on the day of the instance, resources injured in the incident, causes and witnesses are captured. It might be important to know if the incident was related to activity on the critical path or if the incident has occurred in an area congested with other labor and equipment resources. It might be also important to know if the injured resources were new to the company, if they have attended the safety training or attended toolbox meetings, if they were subject to any safety violations or Do Not Walk By notices, etc. Other data that relates to the entities involved in delivering the project, project type and size, project location, project manager, OH&S manager, and other related project details.
Using a project management information system (PMIS) like PMWeb to standardize and automate the hundreds of business processes needed to manage capital construction projects not only helps in starting the process for capturing trust-worthy data but also helps in defining the structure and format of historical data to be captured. This will enable cleaning, verifying, and uploading historical data needed to train and model the problem to be solved using Artificial Intelligence platforms.
When using PMWeb, the organization would have access to the data needed to generate the many metrics, measures, and performance indicators associated with HSE management. Those include for example Average Time Lag in Reporting Incidents, Days Since Last Incidents, Incidents by Category, Incidents by Day of Week, Incidents by Time of Day, Incidents by Month, Incidents by Incident Type, Incidents by Company, Incidents by Injured Resource Name, Incidents by Resource Job Title, Incidents by Resource Years with the Company, Incidents by Resource Age, Incidents by Resource Nationality, Motor Vehicle Incident Rate per 1 Million KMs Driven, Incidents Associated with Critical Path Activities, Incidents by WBS Level, Incidents by Control Account Level. Incidents by Weather Condition Status, Incidents by Site Temperature Range, Incidents Average Per Day During the Month of Ramadan Compared to Other Months, Incidents by Primary Cause, Incidents by Secondary Cause, Incidents by Immediate Cause, Incidents by Contributing Factor, Incidents by Root Cause, Incidents by Risk Likelihood, Incidents by Project Construction Phase, Incidents by Project Location, Incidents by Project Type, Incidents by Project Supervision Consultant, Incidents by Project Manager Name, Incidents by OH&S Manager Name, Incidents Associated with Issued Safety Violations, Incidents Associated with Permit to Work, Incidents Associated with Do Not Walk By Notices, Incidents Associated with Carried Out Checklists among others.
In addition, data will become available to calculate other measures like those for Days without Lost Time Incidents, Top 10 Projects by LTIR, LTIR by Month, Number of Missed Day, Number of Incidents for Top 10 Projects with Delays to Completion Date % to Baseline Duration, Number of Incidents for Top 10 Projects with Over Budget % to Baseline Budget, Resource Injuries by Body Part, Resource Injuries by Root Cause of Injury, Resource Injuries by Primary Cause of Injury, Resource Injuries by Secondary Cause of Injury, Resource Injuries by Immediate Cause of Injury, Resource Injuries by Contributing Factor of Injury, etc.
To have access to the data used in creating those measures and performance indicators, PMWeb will be used to manage the business processes needed to capture the data. Those would include the processes for defining the labor and equipment resources deployed on projects, list of companies what resources working at each company, the details of projects to be executed or executed by the company, baseline and updated project schedules, daily reports, safety incidents, safety violations, EHS checklists, permits to work, gate passes, toolbox and safety meetings and others.
Since the main focus of this AI solution will be safety incidents, then this business process should be designed in a format that enables capturing the needed data as well as associating data from other business processes managed in PMWeb. PMWeb safety incident module comes ready with most of the needed fields to align the captured safety incidents with the HSE risk register. These include incident subject, date and time of occurrence as well as reported on, relevant work breakdown structure (WBS) level, incident type, and category, incident description, and details of works in progress at that location.
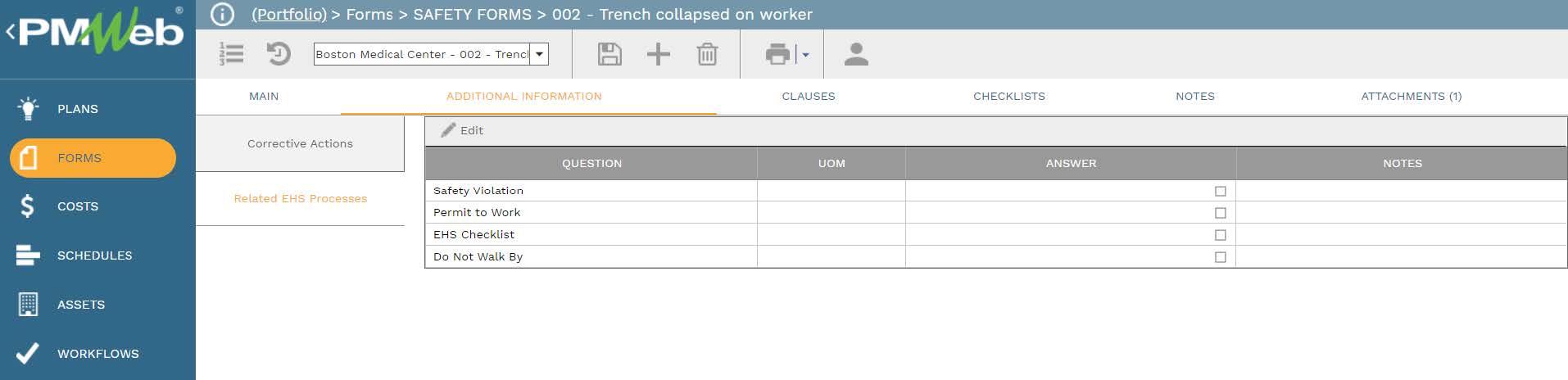
In addition, the form will be appended with ten new fields to capture other needed data fields. Three of those fields will be with a predefined list of values for assessing the safety incident impact on human resources, work on-site and cost implications. Each field will have four predefined values that are aligned with the Accident Severity Categories being 4 for Catastrophic, 3 for Critical, 2 for Marginal, and 1 for Negligible.
Further, the form will be appended with five fields for reporting the causes of the safety incidents. Those will be the fields for the primary cause, secondary cause, immediate cause, and contributing factors. The fifth cause, the root cause, will be completed by the safety manager to associate the safety incident with the HSE risk that will result from this cause. Those five causes will have the same predefined list of all causes that will be standard for all projects managed by the organization. The last two additional user-defined fields will be for the project schedule activity as well as cost breakdown structure (CBS) or control associated with the activity.
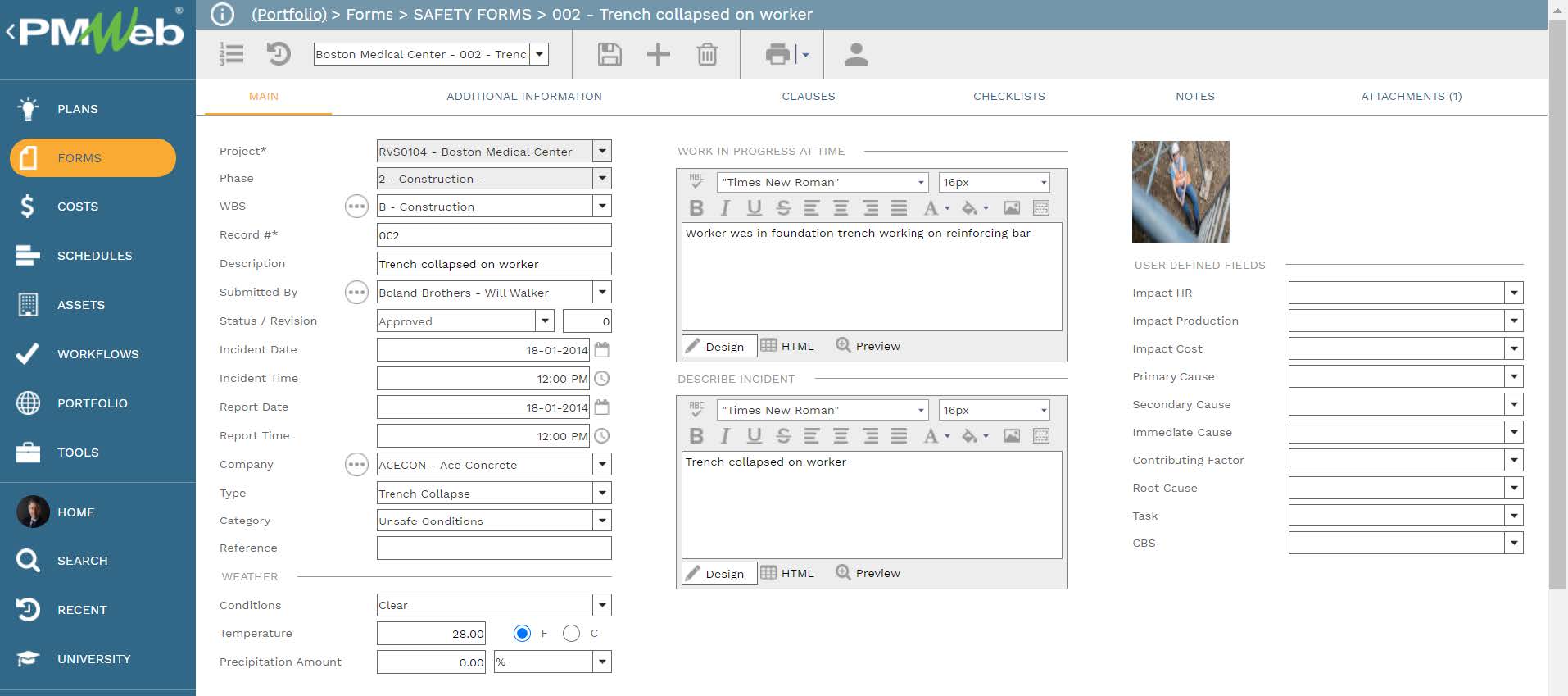
In addition, the form has three tables to capture the details of the resources who were injured in the safety incident. For each resource, PMWeb allows capturing the resource name, company, resource classification, age, years of experience, injury type, injured body part, injury severity, current conditions, and notes. Most of those fields will be selected from a predefined list of values.
Further, there will be a section to record details of the reported causes. For each reported cause, PMWeb allows adding the description and notes. This section also enables adding other causes in addition to the five causes categories that have contributed to the occurred safety incident. The provided description and notes for each reported cause are of great importance when analyzing the causes and impacts associated with the reported safety incident. In addition, there will be a section detailing the individuals who have witnessed the safety incident.
The safety incident form could also have more data fields if needed. For example, a new group of user-defined fields can be added to confirm if the safety incident has any relation to a work permit, safety violation, EHS checklist, Do Not Wall By, or any other EHS business process. The actual EHS business process transaction will be linked to their relevant safety incident transaction using the attachment tab on the form. Other groups of additional information can be added to the form if required.
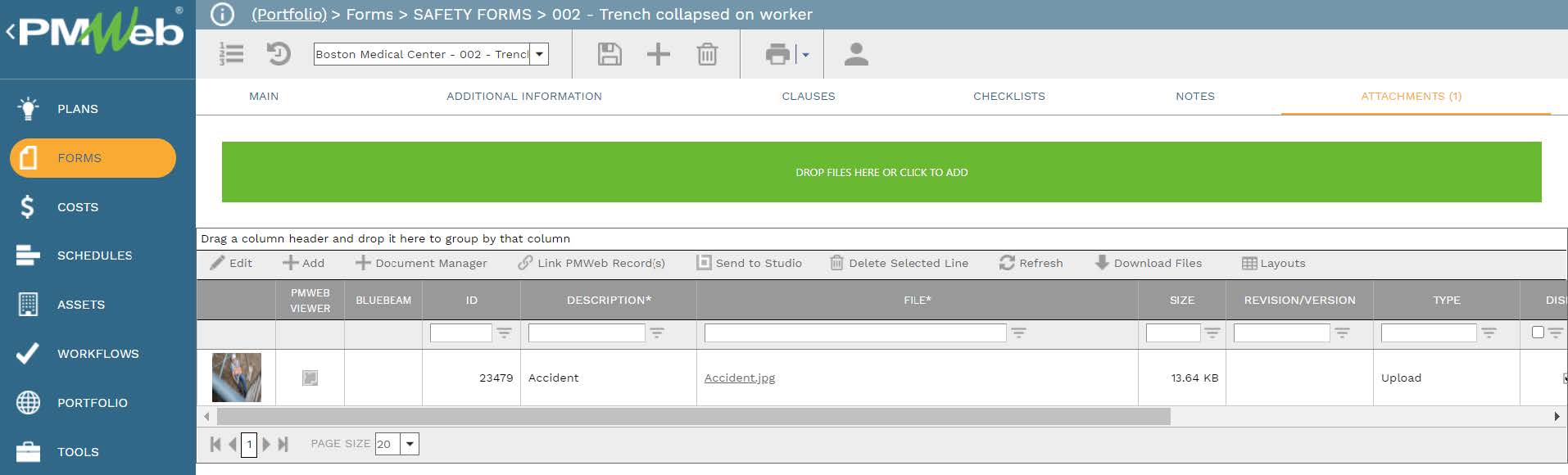
In addition to the linked EHS records, the attachment tab will be also used to attach all supportive documents like pictures of the injured people, vehicle and equipment involved in the accident, accident location, police report, medical report among others. Since PMWeb is a zero-footprint application, it can be accessed from any smart mobile device like an iPad or a smart phone where pictures and videos can be taken and directly attached to the safety incident form. It is highly recommended that all those supportive documents are uploaded and stored into their relevant folder or subfolder in the PMWeb document management repository.
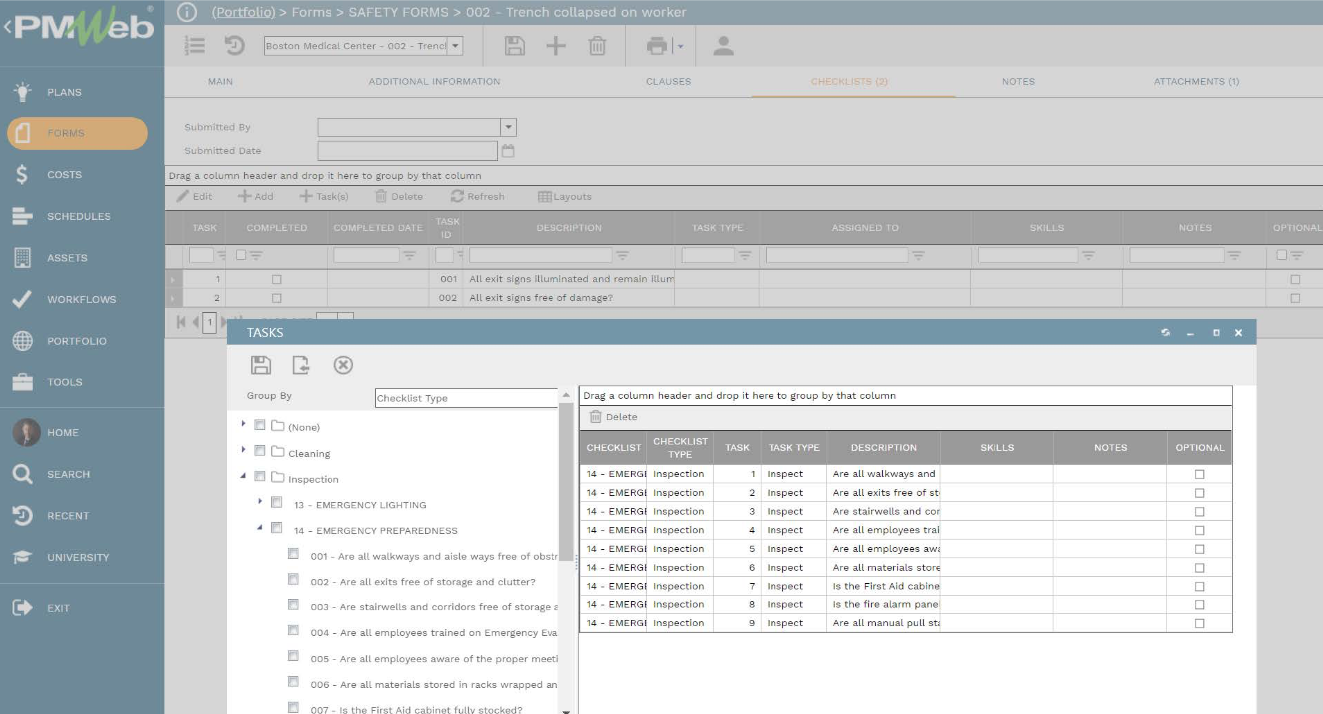
Although the organization can create a new form for the corrective actions business process, nevertheless, it is possible to use the Checklist tab on the Safety Incident form to capture those details. PMWeb allows creating a pre-defined list of possible corrective measures from each type of safety incident to expedite the process in determining and selecting the best-suited corrective actions. Of course, the PMWeb user can add more corrective actions for those predefined actions that could be specific to the reported safety incident as well as delete predefined corrective actions that do not apply to the incident.
For each corrective action, PMWeb allows defining the corrective action, adding notes, corrective action type (immediate or near-future), assigned to who, completed on date, and completion confirmation. Each corrective action can be detailed into sub-actions with the same data fields for the main corrective action. Again, this data is very important to train the artificial intelligence platform on possible corrective actions to reduce the likelihood and maybe the impact of those safety incidents.
PMWeb also allows all those involved in the safety incident process to add notes and comments that they believe could add more knowledge on what has happened. Each note will have the PMWeb username who has shared the note, the date and time of the note, the note subject, and the note details. Since PMWeb allows providing those notes on rich text forms, pictures can be embedded in the notes as well as text can be formatted in the desired format.
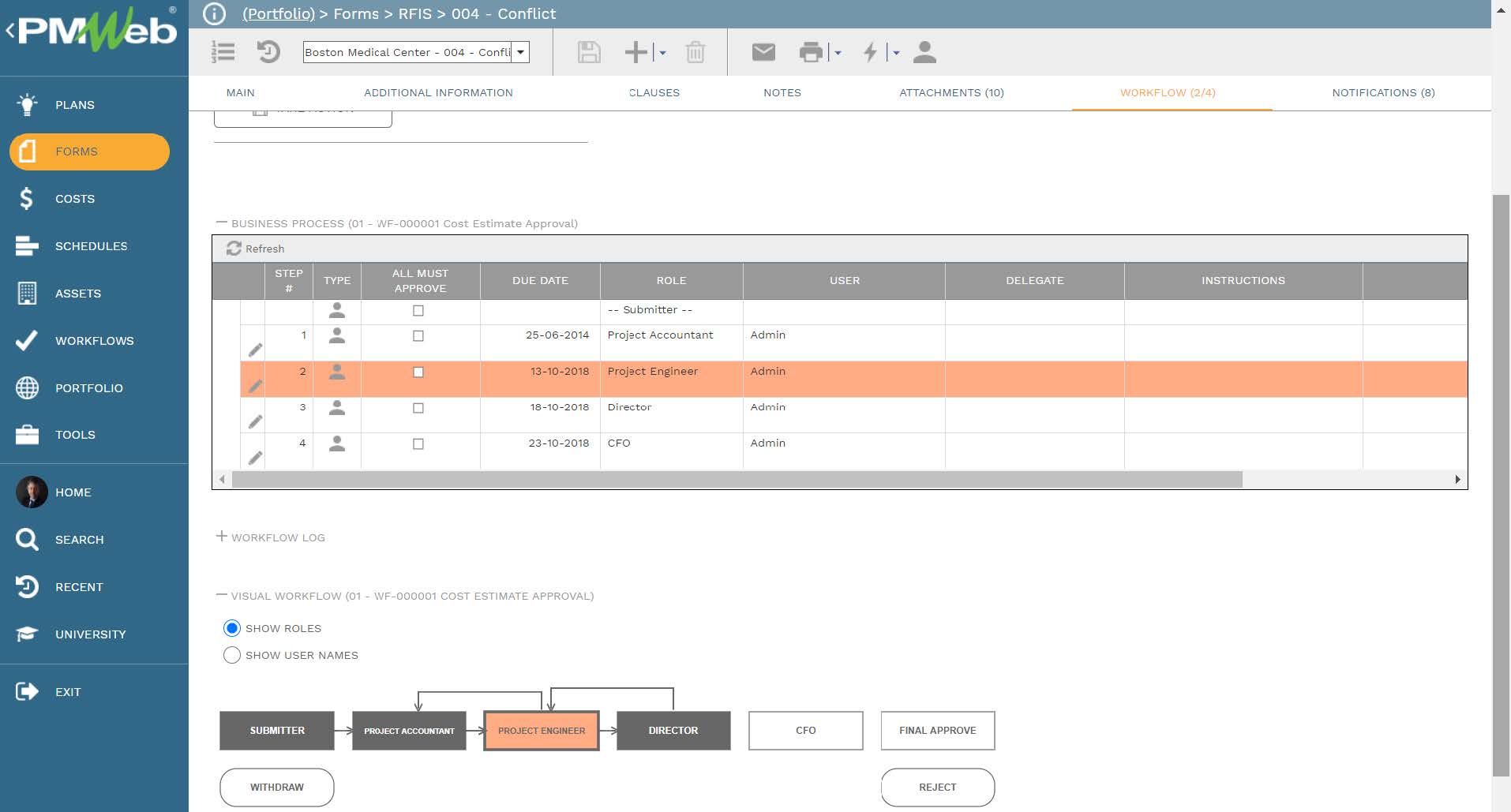
To ensure that the data captured in each safety incident transaction has been provided, reviewed, and approved by the project team member assigned to do so, a workflow will be assigned to the safety incident form. The workflow will map the sequence for performing those tasks, the duration for each task, to be performed by who and who should be copied on the task. The workflow will enforce accountability in providing the project’s data.
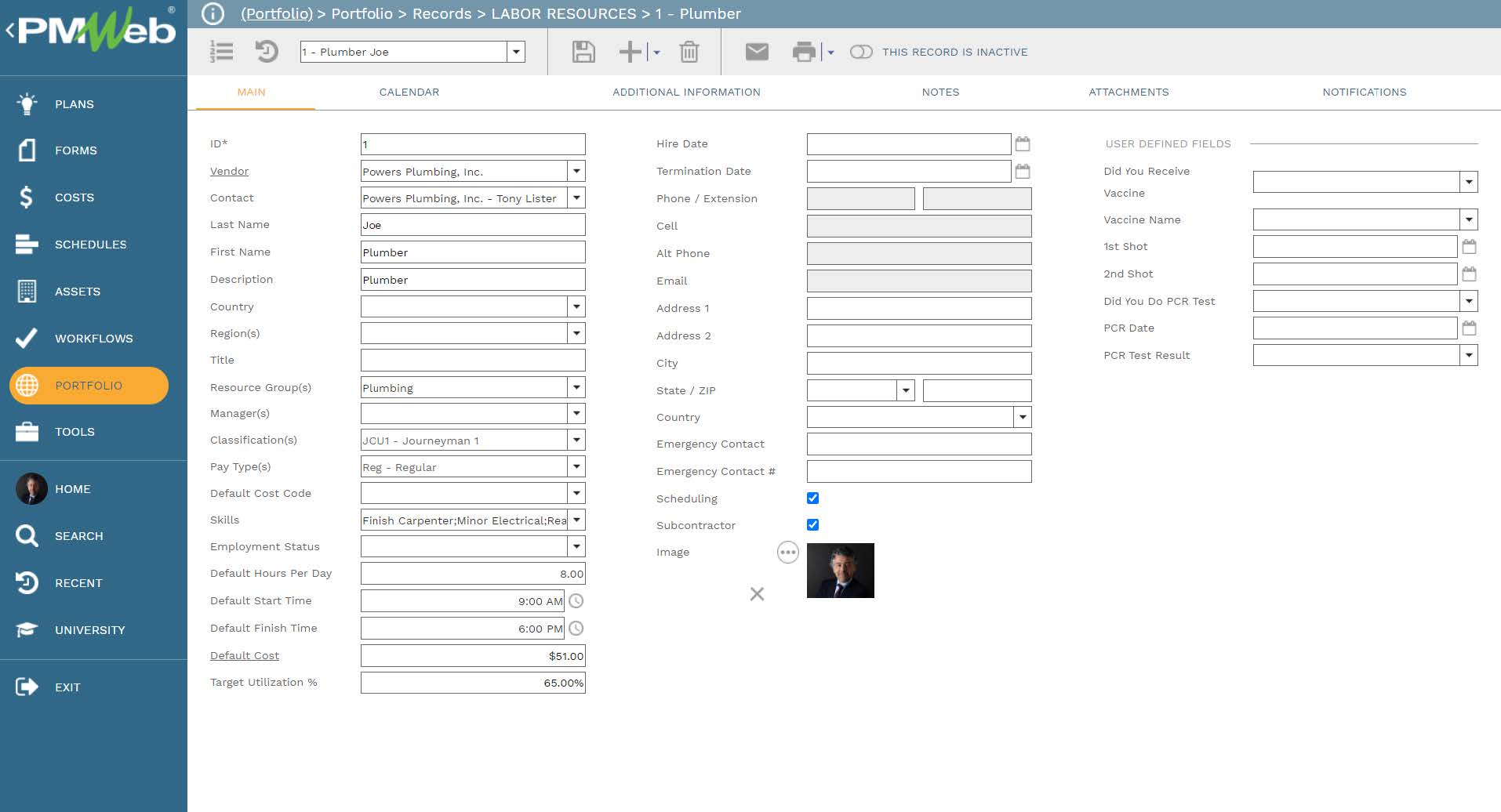
In addition to the data captured in the safety incident process, there are other data fields captured in other PMWeb business processes data tables that also need to be extracted by the artificial intelligence (AI) platform. The first one of those is the labor and equipment resources directory. Although the safety incident will capture the name of each resource injured in the incident or witnessed the incident, nevertheless, PMWeb resource module will be used to capture all other resource details that could add value to the artificial intelligence platform.
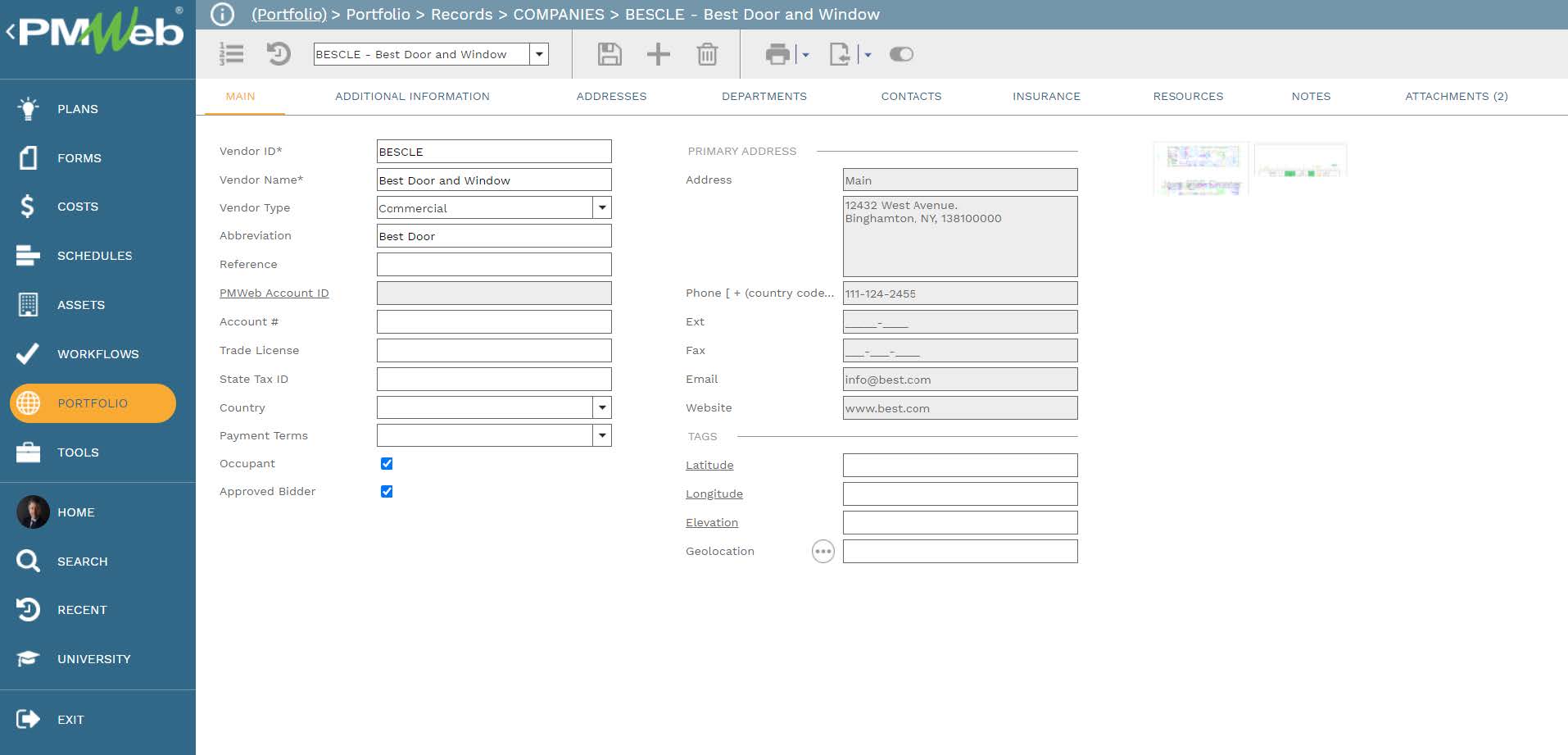
Another PMWeb data table that will be needed to grow the volume of relevant data needed by the AI solution will be the companies’ data. Those are the companies that the resources involved in the accident or witnessed the accident works for. The data will also include the details of the project owner and companies used to manage and supervise the project.
Of course, there is a need to have a complete definition of the project that the captured data belongs. PMWeb project module will be used to capture details on the project type, size, category, sponsor, owner, consultant, contractor, project manager, planned start and finish dates, duration, budget cost, the scope of work, and other details that can better describe the project. In addition, PMWeb allows defining the project’s geospatial coordinates to identify its location. Additional fields can be added to detail the project’s built-up area, number of floors, components, etc.
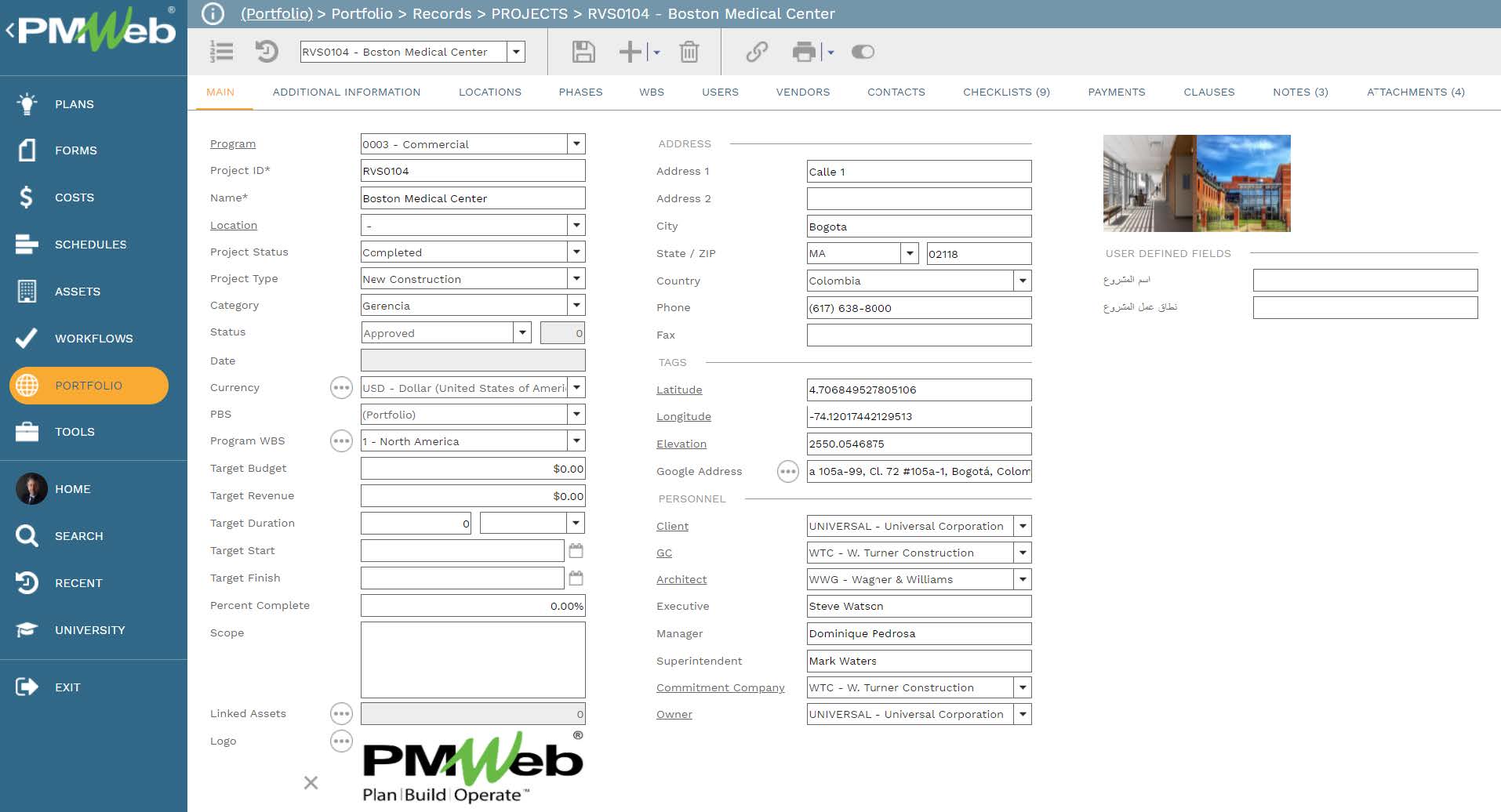
The baseline integrated project schedule and periodical schedule updates are another data table that will be needed for the AI platform. PMWeb scheduling module will be used to capture the baseline schedule and updates. Each safety incident will be linked with the relevant project schedule activity as well as WBS level.
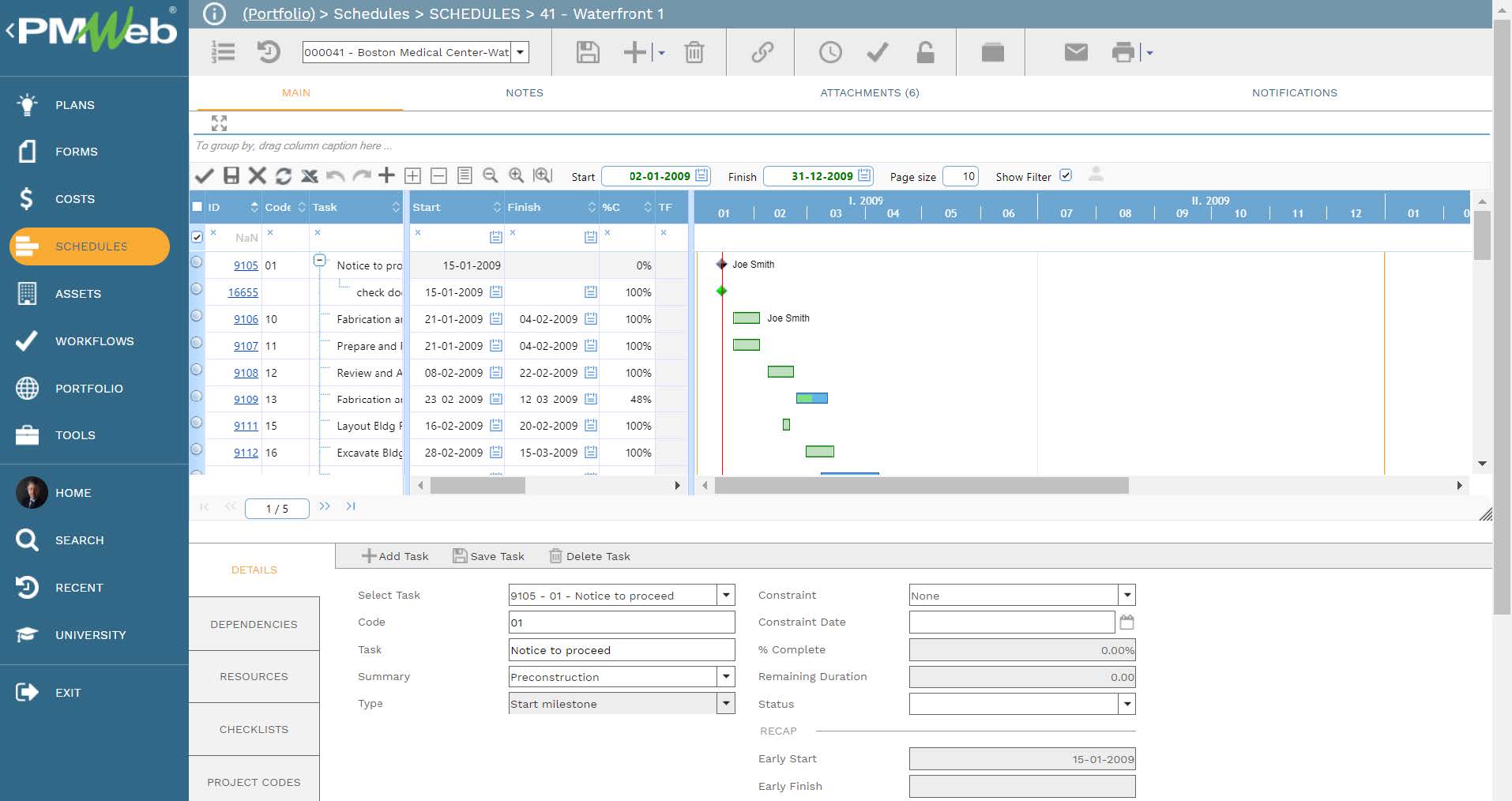
The daily report module is another important source of data for artificial intelligence. The daily report will capture the details of everyday activities performed and labor and equipment resources deployed on the project construction site and in particular the location where the safety incident took place. The daily report will detail if any hazardous activities were being executed at the safety incident location and if the location was congested with resources including equipment resources. The daily report will also capture any safety-related observation at the area where the work was being performed.
The resources captured in the daily report and similar to the resources captured in the safety incident report will be the resources defined in the PMWeb resources dictionary. The same will also apply to the companies used in those two forms which will be defined in the companies module.
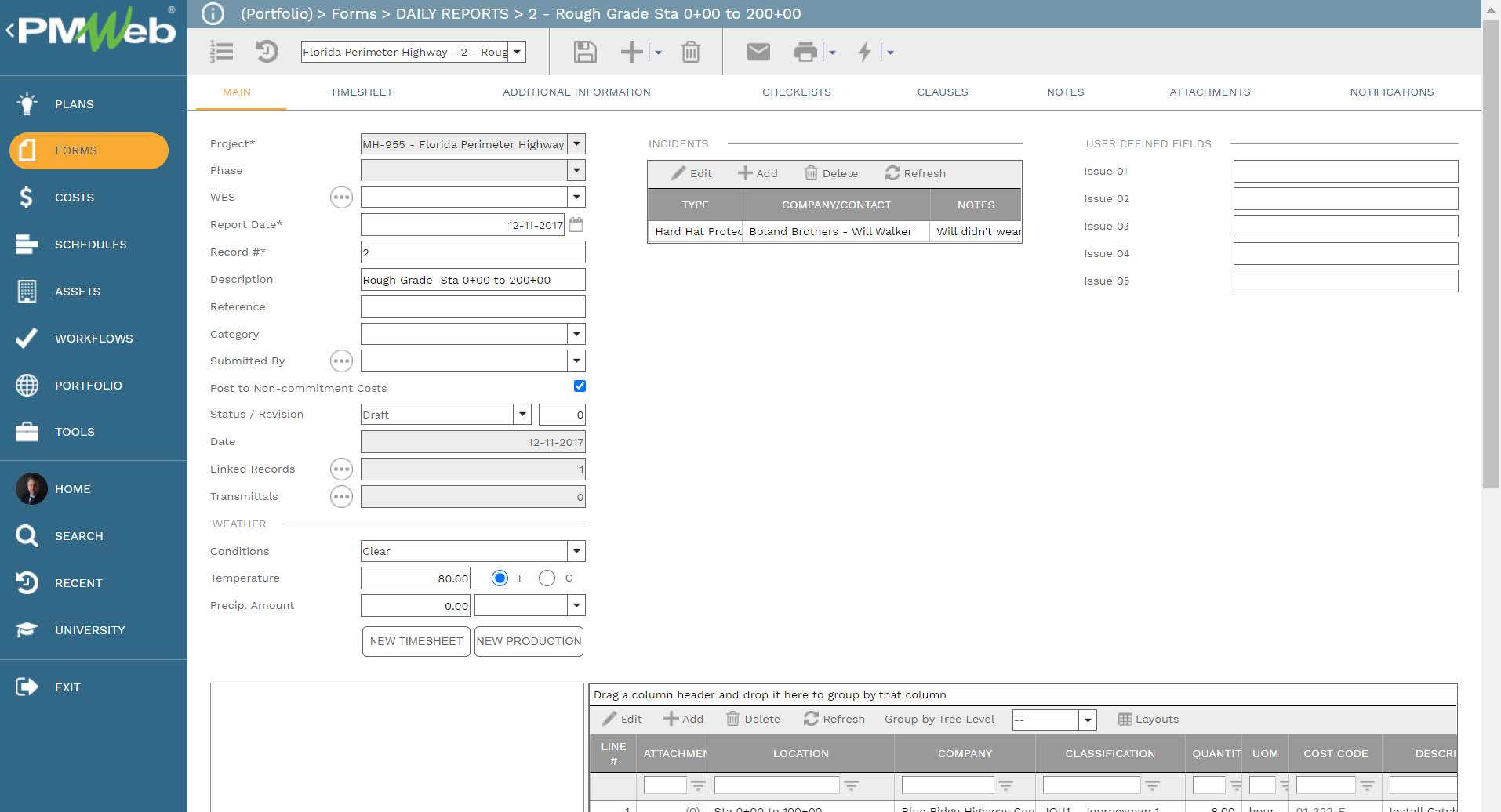
For other EHS related business processes which might be relevant to the reported safety incident transaction like permits to work, gate pass, safety violation, EHS checklists, EHS self-assessment checklists, Do Not Walk By, HSE Audit, Non-Compliance Report (NCR), and others will be created using PMWeb Visual Custom Form Builder. Those forms will be designed to include all necessary data fields to ensure that those business processes are performed under EHS Management Plan.
The supportive documents that are attached to all business processes, as well as documents that could be relevant to EHS business processes and other project management business processes, will be uploaded and stored in the relevant folder or subfolder in the PMWeb document management repository. The metadata and attributes that relate to each uploaded document will be captured and assigned to the document.
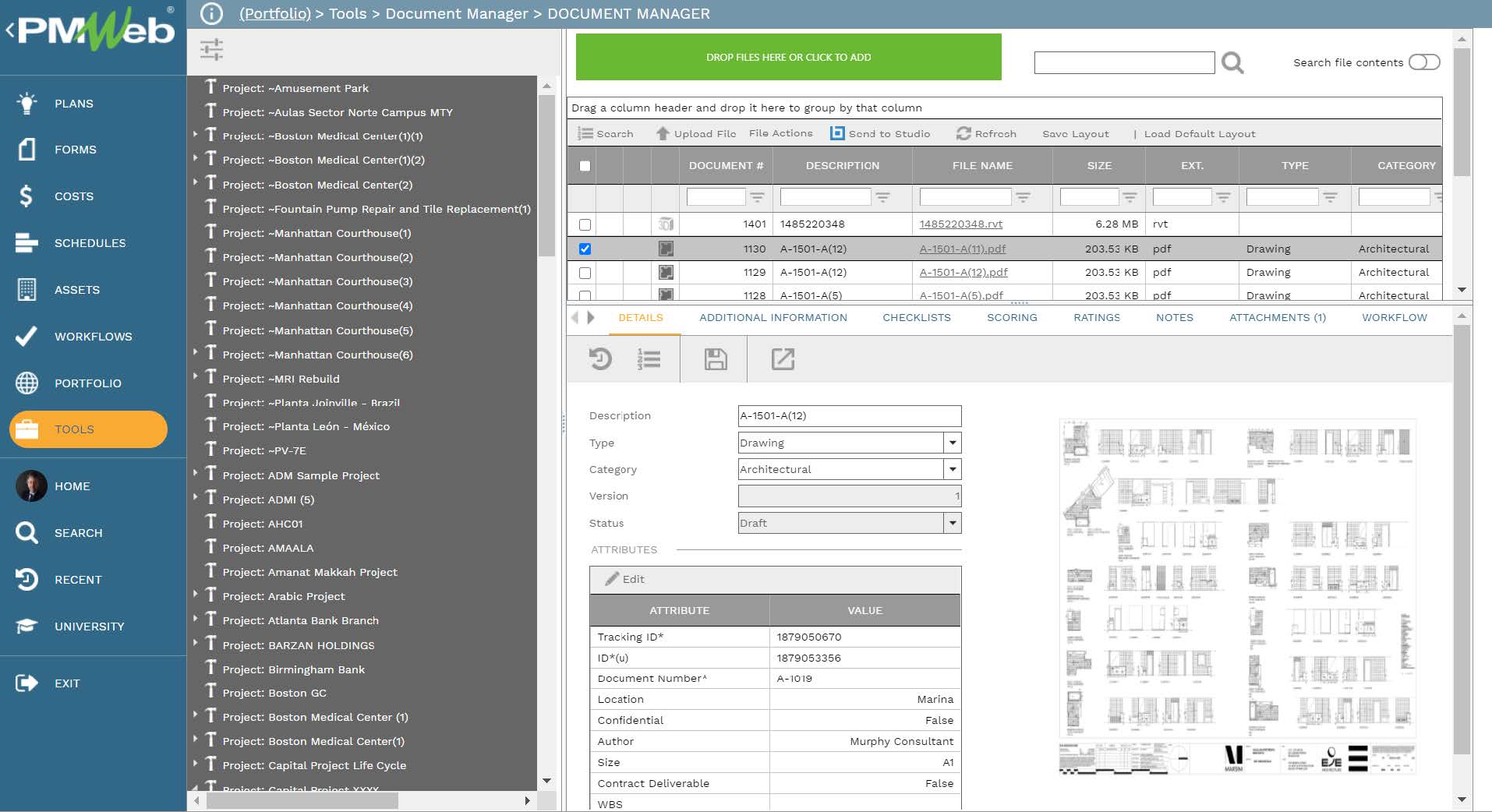
Regardless of the data warehouse that will be used by the Artificial Intelligence solution, the data captured in PMWeb data tables will be extracted, transferred, and loaded into this central data warehouse. The data warehouse solution will also enable extracting, loading, transferring, de-normalize, cleanse and validate historical data captured from other data sources including data from legacy systems that the organization might have access to. This data will become the data that will be needed to train the Artificial Intelligence solution to better predict results, proposed decisions, and share lessons learned with the project stakeholders.
The same approach detailed above to build the HSE knowledge needed to train an AI solution will be also repeated with the other business processes needed to provide knowledge on other project management areas to provide better predictability on the project’s completion date and cost at completion. For example, PMWeb business processes for claim notices, extension of time requests, shop drawings and other technical submittals, request for information, time impact analysis, cost estimate, budget, budget adjustments, and transfers, received bid proposals, awarded contracts, potential change orders, change orders, interim payment certificates, forecast to complete analysis and others will be used to capture the needed data to provide the information required to build the required knowledge.
Although those business processes will be initiated, reviewed, and approved by different individuals than those involved in the EHS business processes, nevertheless, all those business processes have at least two things in common. The first is that all of the data generated from the different transactions executed for each business process will be stored on a single data source and not on dispersed data silos while the second thing in common is that all those business processes will have the same backbone to align the captured date with the project’s control accounts and schedule activities. This will be one of the main data sources that the artificial intelligence platform needs to access to have the relevant wisdom to propose actions or predict future outcomes.