One must admit that the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown has allowed many of us to attend events that usually we could not spare the time to attend. One of those recent events that I have enjoyed attending was titled “The Dangers of Dirty Data and its Consequences” which was hosted by Bernie Smith and Susan Walsh. Although the presentation did not focus on construction projects, nevertheless, the issues raised and the consequences of dirty data are very much applicable to construction projects as well as other types of projects.
Dirty Data and its Consequences
Ms. Walsh identified dirty data as misspelled words, incorrect descriptions, missing codes, adding data in wrong columns or fields, no standard units of measure, currency issues, date and currency formatting issues, duplicate data among others. During the webinar, Ms. Walsh detailed the best practices to spot and identify dirty data and actions that need to be taken to clean the dirty data. This data clean-up is a prerequisite to ensuring that it can be used to provide the needed insight to make better and faster-informed decisions. In summary, for data to be of use, the data needs to be consistent, organized, accurate and trustworthy; or as called by Ms. Walsh, data needs to have a COAT.
The actions detailed in the webinar to spot, identify and clean the dirty data was more from a reactive or after-the-fact perspective. It has focused on how data, and mainly financial and sales data, captured in MS Excel and other applications can be inspected, verified and corrected before it can become usable for executives to make informed decisions. This clean-up task is usually done on quarterly or monthly basis depending on the need.
Nevertheless, this periodical after-the-fact dirty data clean-up process will not work when it comes to delivering capital projects where the types and volume of captured data are many. Capital projects’ data include schedule, cost, quality, HSE, risks, communications, procurement among others. Further, data on projects gets captured and populated almost every hour, every day of the week. Decision makers do not have the privilege to wait for a month or even days to have the captured data inspected, verified and corrected. Decisions need to be made almost immediately when there is a need for an action. The consequences of bad decisions that could lead to wrong actions could be drastic, as they could result in budget overrun, delayed completion date, suspension and termination of contracts, low quality projects among others that will increase the chances for project’s failure risk.
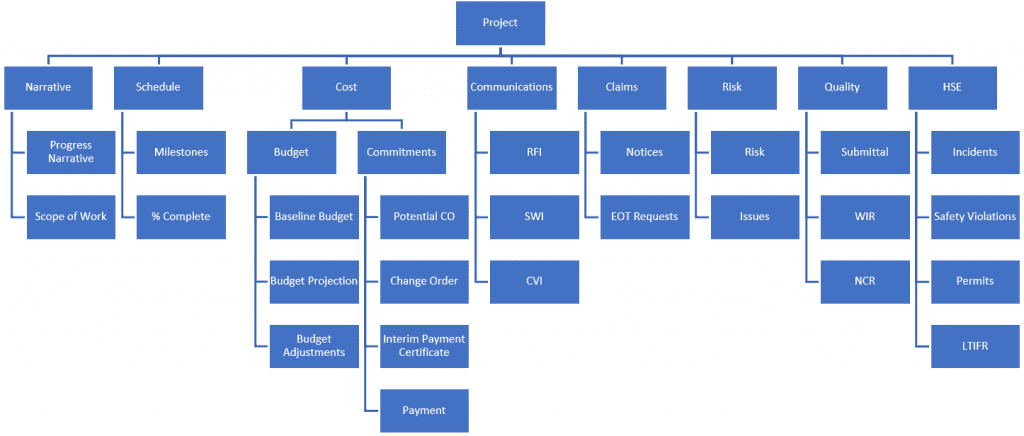
Therefore, capital projects need to enforce proactive measures to eliminate the likelihood of having dirty data and the consequences of this risk. This does not require a rocket-science solution. We simply need to have a solution where all project data will be captured and stored using pre-defined forms with all needed fields. Those data fields will be pre-configured to enforce providing the data in the correct format. In addition, some data fields could include the option of having pre-defined list of values to enforce selecting correctly spelled and defined values.
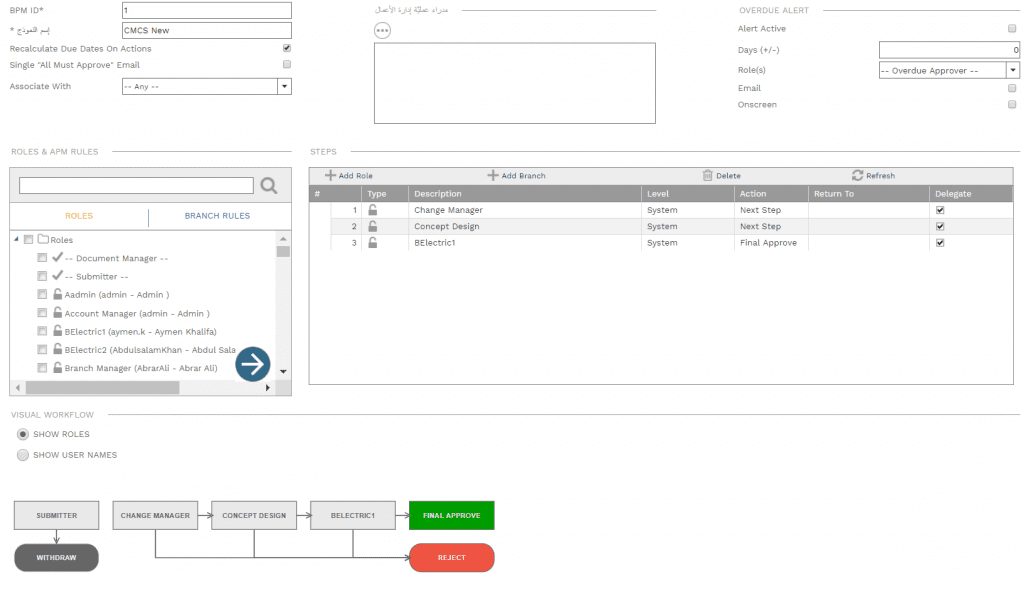
Access to those input forms and the data fields within each form will be provided to only authorized individuals where they will be held accountable to provide the needed clean data along with all supportive documents. Those forms can be accessed by those authorized individuals anytime, anywhere using any device to ensure real-time clean data capturing. Each authorized individual will have unique login and password credentials. Those forms need to also have a workflow assigned to them to define the sequence for providing and verifying the reported data. Finally, the solution should enable reviewing, analyzing and reporting the captured data in any desired form and format to fulfill the reporting needs of project stakeholders.
Using a Project Management Information System (PMIS) like PMWeb the objective of having real-time clean data can be easily achieved. PMWeb will be the single repository for all types of data for programs and projects managed by the organization. Access to PMWeb will be provided to authorized individuals representing the different entities involved in delivering the organization’s capital project investments. Being 100% web-enabled, those individuals can access those forms regardless of where they are physically located. The data captured in PMWeb can be reported on in any desired form and format either using PMWeb business intelligence reporting tool or any third-party business intelligence and data visualization tool like MS Power BI, where PMWeb data can be associated with third-party data like those from ESRI geospatial data to increase the value of the clean data by providing more information and better insight.
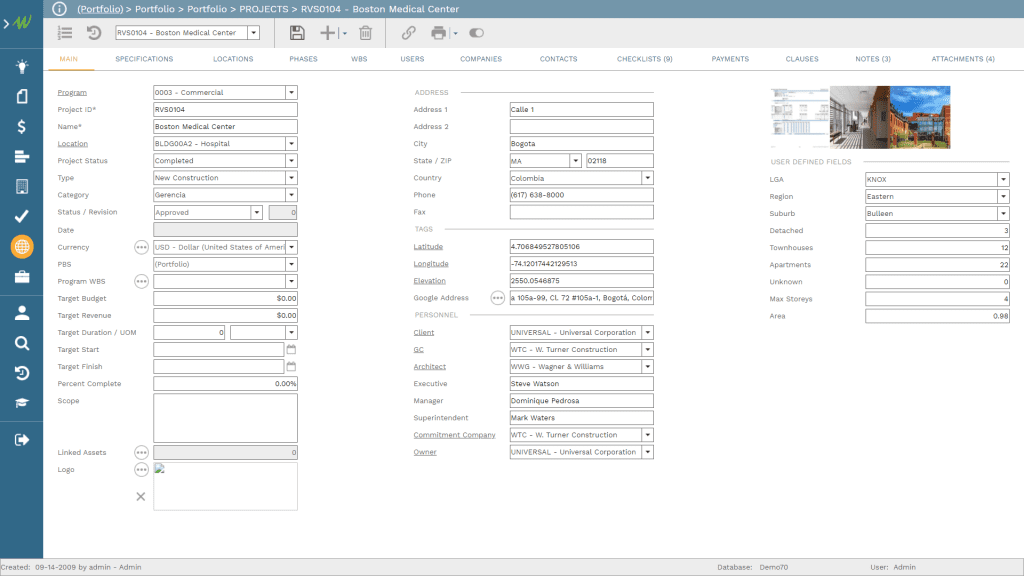
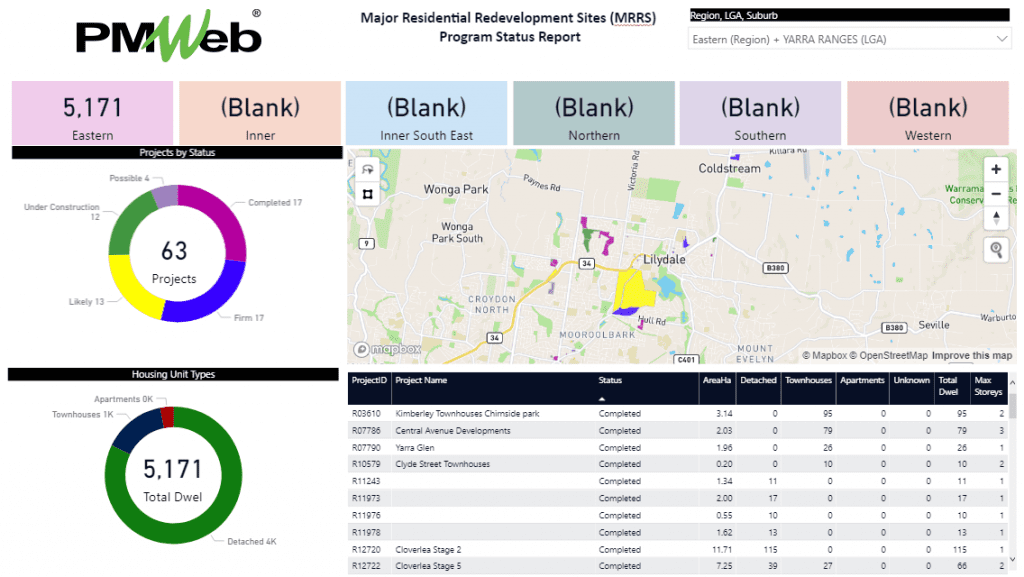
To start with, each capital project investment details need to be captured in PMWeb. The data will include the project name, location, scope of work, components, key stakeholders among others. PMWeb default project module will be used to capture this information where additional fields will be created to capture other critical data needed by the organization but might not be available by default in PMWeb. For example, the data associated with almost 3,500 housing projects needed by the Victorian Government, Australia to manage their major residential redevelopment sites (MRRS) program will be captured in PMWeb. This data includes the project start, number of dwell units included in each project by type, number of floor levels, plot area, street location, region, local government area (LGA) name, suburb, etc.
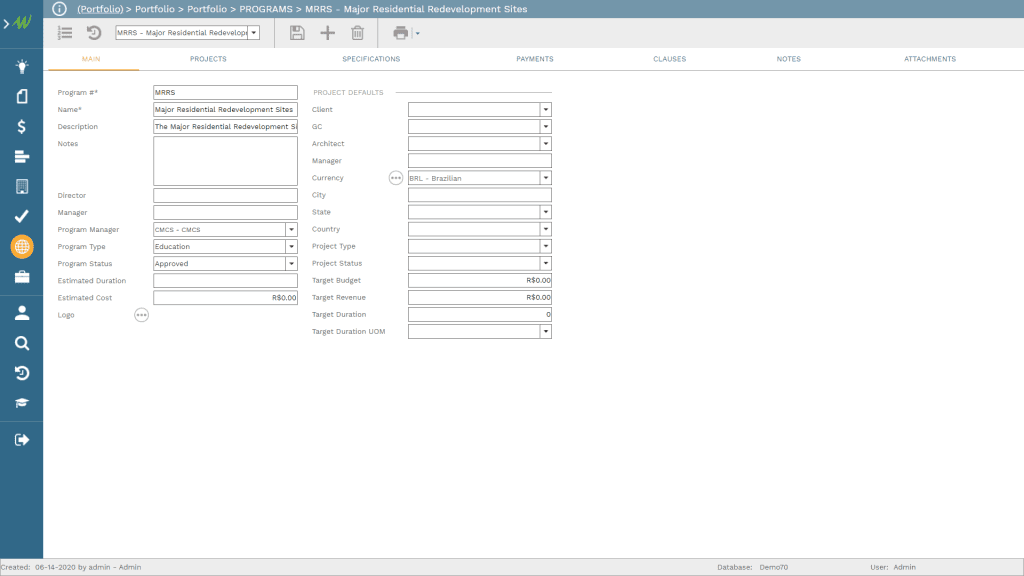
In addition, PMWeb program module will be used to add the major residential redevelopment sites (MRRS) program and link the 3,500 housing projects to this program. This will enable the Victorian Government, as an example, to have a single data repository for their other urban development programs and projects for healthcare, education, entertainment, retail, commercial, green parks, streets, roads, rail, infrastructure, utility among others.
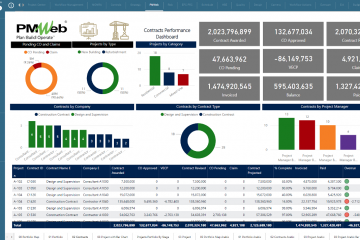
Associating the projects’ data with the geospatial data captured in ESRI which could include project boundaries, perimeter length among others, will provide better visualization and analysis of the projects’ data. In addition, ESRI could also include data that relates to the demographics of each suburb, water and utilities consumption and other data that could help in better understanding the impact of the current projects and decisions to be made for future developments.
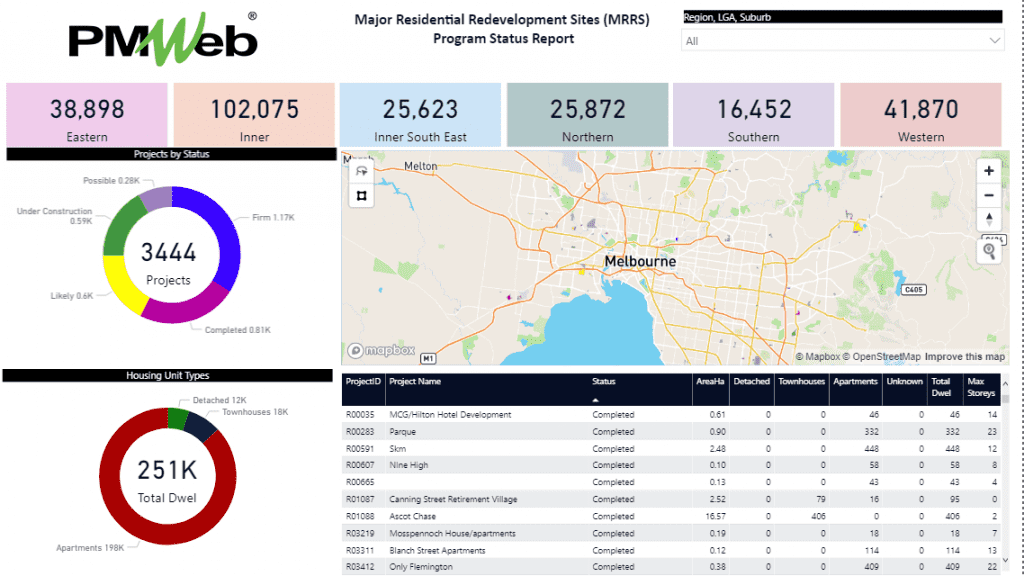
The report can be designed with the needed filters to enable selecting the desired information to be reviewed, analyzed and reported on. For example, selecting a specific suburb, this will modify the total number of dwelling units to reflect only those for projects that are located in the suburbs of one of the local government areas (LGA). In addition, the two donut visuals for projects by status and housing unit types will be adjusted to reflect the projects in the selected suburb within a region. The two donuts also display the total number of projects and dwelling units as per the selected filter. In addition, the displayed map will automatically zoom to show the boundaries of the selected projects which will be colored by the status of the project. Finally, the scorecard that includes the projects’ details will be filtered to display only the selected projects.
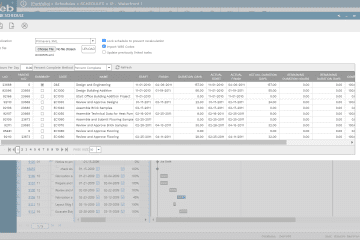
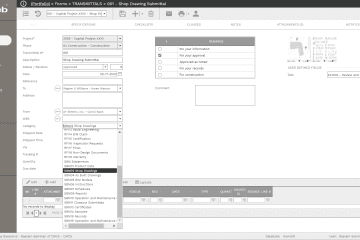
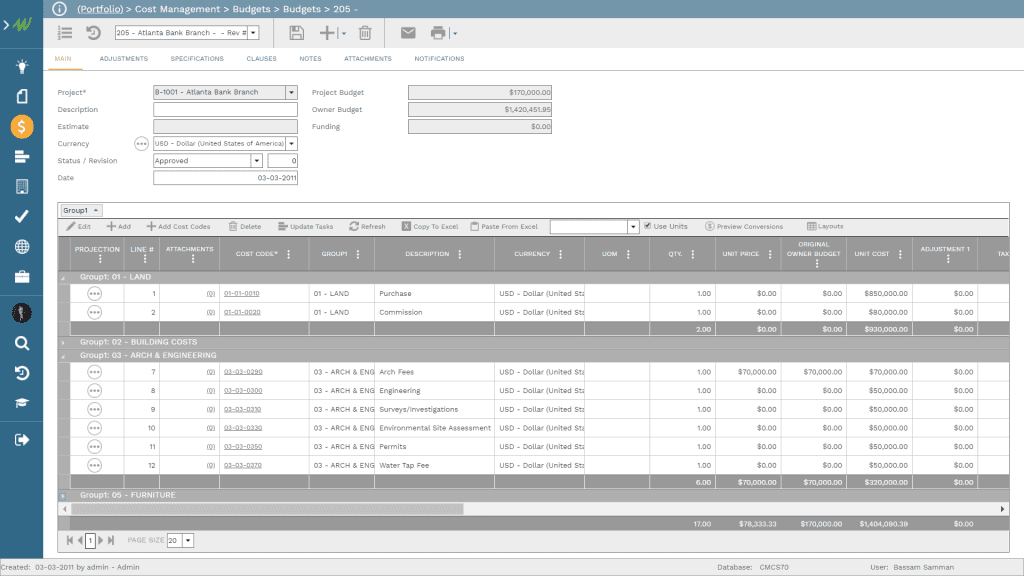
Each project management process form used in PMWeb requires having the project name that the captured data is associated with. Those include the processes for schedule milestones, schedule updates, budget, budget adjustments, commitments, potential change orders, change orders, interim payment certificates (IPC), payments against IPC, risks, issues, submittals, work inspection requests, site work instructions, non-compliance reports, testing and commissioning inspections, punch lists, request for information, site work instructions, meeting minutes, confirmation of verbal instructions, safety incidents, safety violations, permits for work, gate passes, daily reports among many others. Similar to the project form, PMWeb comes ready with most of the forms needed to capture this data. In addition, custom forms can be created to capture all other data types that are not available by default in PMWeb.
All those forms, whether available by default or created using the custom form builder can be attached with uploaded documents that will be stored in the PMWeb Document Management Repository. Those documents could include drawings, certificates, tables, pictures, videos among others. In addition, links to other relevant PMWeb records and imported MS Outlook emails can be added.
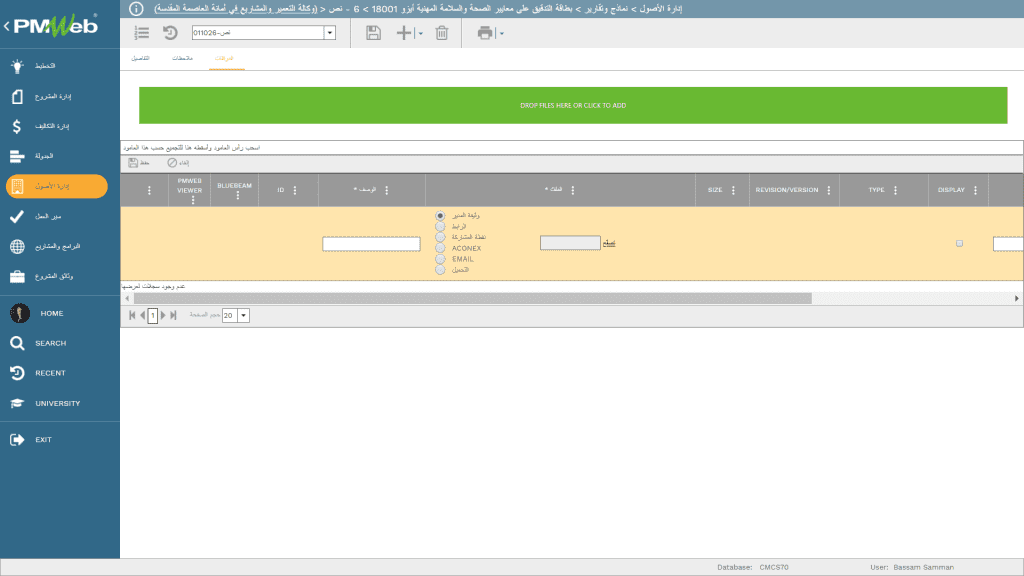
Further, workflow can be assigned to each form to formalize the review and approval process needed for clean data. The workflow will identify the sequence, duration and responsibility for performing the review and approval tasks. In addition, the workflow could include conditions to enforce the authority approval levels associated with some processes, like those for approving change orders.